|
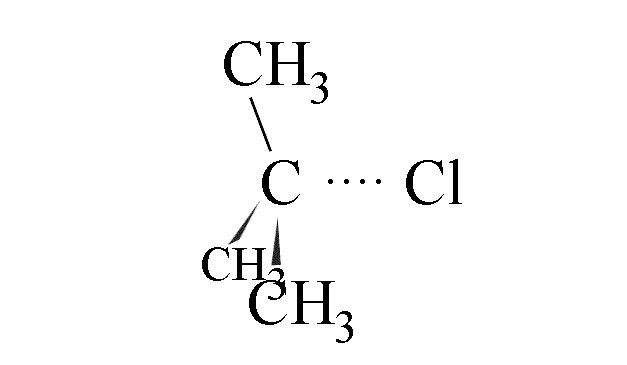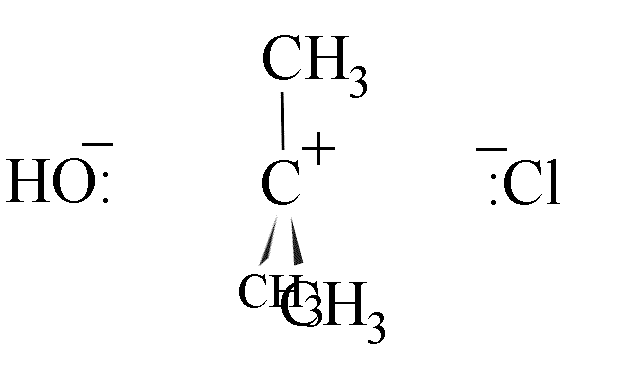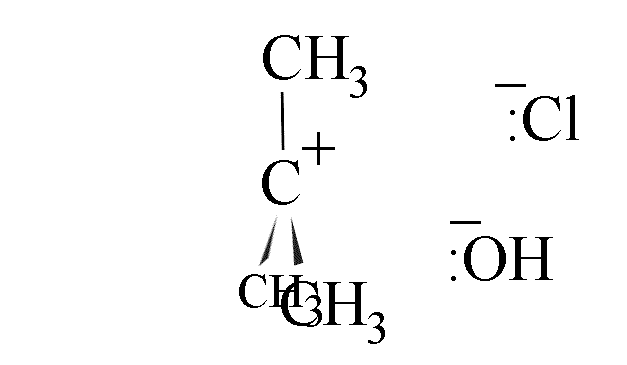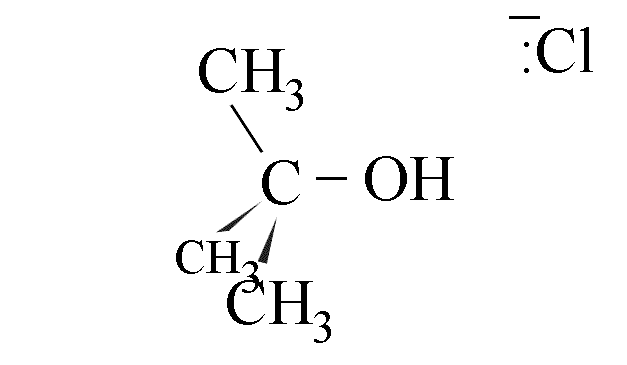
- The C-Cl bond in the halogenoalkane starts to lengthen and weaken
- The chloride ion is eventually detached from the carbon atom and a flat carbocation
forms. This is the rate determining step.
- The hydroxide ion could attack from the left-hand side, leading to inversion of the
configuration of the carbon skeleton; or
- attack could come from the right, leading to retention of configuration.
- The use of a chiral halogenoalkane in this reaction leads to production of a
racemic mixture if the amount of attack from each side is equal. The hindrance caused by
the departing cloride ion gives about 40% attack from the right and 60% from the left,
however.
|
